Forecasting Reservoir Water Levels Using Deep Neural Networks: A Case Study of Angat Dam in the Philippines
Jan 1, 2022· ,,
,, ,·
0 min read
,·
0 min read
S. Ibañez
C. Monterola
C.V. Dajac
M. Liponhay
E.F. Legara
J.M. Esteban
Abstract
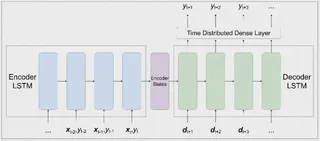
Forecasting reservoir water levels is essential in water supply management, impacting both operations and intervention strategies. This paper examines the short-term and long-term forecasting performance of several statistical and machine learning-based methods for predicting the water levels of the Angat Dam in the Philippines. A total of six forecasting methods are compared: naïve/persistence; seasonal mean; autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA); gradient boosting machines (GBM); and two deep neural networks (DNN) using a long short-term memory-based (LSTM) encoder-decoder architecture: a univariate model (DNN-U) and a multivariate model (DNN-M). Daily historical water levels from 2001 to 2021 are used in predicting future water levels. In addition, we include meteorological data (rainfall and the Oceanic Niño Index) and irrigation data as exogenous variables. To evaluate the forecast accuracy of our methods, we use a time series cross-validation approach to establish a more robust estimate of the error statistics. Our results show that our DNN-U model has the best accuracy in the 1-day-ahead scenario with a mean absolute error (MAE) and root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.2 m. In the 30-day-, 90-day-, and 180-day-ahead scenarios, the DNN-M shows the best performance with MAE (RMSE) scores of 2.9 (3.3), 5.1 (6.0), and 6.7 (8.1) meters, respectively. Additionally, we demonstrate that further improvements in performance are possible by scanning over all possible combinations of the exogenous variables and only using a subset of them as features. In summary, we provide a comprehensive framework for evaluating water level forecasting by defining a baseline accuracy, analyzing performance across multiple prediction horizons, using time series cross-validation to assess accuracy and uncertainty, and examining the effects of exogenous variables on forecasting performance. In the process, our work addresses several notable gaps in the methodologies of previous works.
Type
Publication
Water