Earning potential in multilevel marketing enterprises
Apr 7, 2008·
 ,,,·
0 min read
,,,·
0 min read
E.F. Legara
C. Monterola
D.E. Juanico
M. Litong-Palima
C. Saloma
Abstract
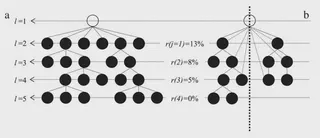
Government regulators and other concerned citizens warily view multilevel marketing enterprises (MLM) because of their close operational resemblance to exploitative pyramid schemes. We analyze two types of MLM network architectures — the unilevel and binary, in terms of growth behavior and earning potential among members. We show that network growth decelerates after reaching a size threshold, contrary to claims of unrestricted growth by MLM recruiters. We have also found that the earning potential in binary MLM’s obey the Pareto “80–20” rule, implying an earning opportunity that is strongly biased against the most recent members. On the other hand, unilevel MLM’s do not exhibit the Pareto earning distribution and earning potential is independent of member position in the network. Our analytical results agree well with field data taken from real-world MLM’s in the Philippines. Our analysis is generally valid and can be applied to other MLM architectures
Type
Publication
Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications